A Virus is small collection of genetic code,either DNA or RNA surrounded by protein coat that replicate only inside the living cell of an organism.
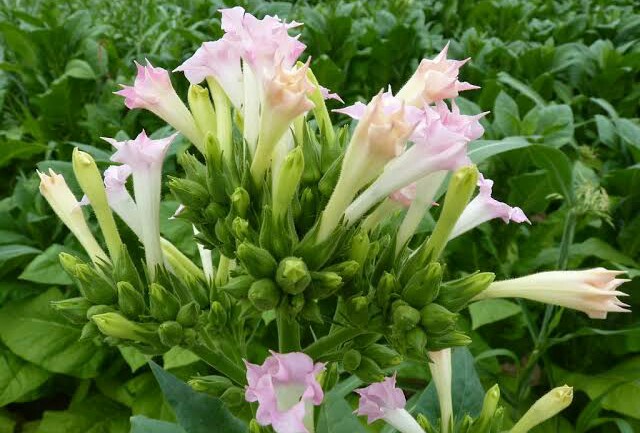
Discovery- The first virus was discovered by Russian botanist D.Iwanovsky in 1892. it cause in tobacco plant(Nicotiana tabacum) a fatal disease called mosaic disease because the infected leaves have a spotted appearance . The causative agent has been namaed tobacco mosaic virus(TMV). Iwanovsky found that the disease would be transmitted to healthy plants by daubing(smearing) their leaves with the juice (sap) of disease plants.

Morphology- Size– The viruses are too small to be seen with a light microscope,they can only photographed only with an electron microscope. Shape- viruses vary in form too. They may be spherical ,cuboidal,polyhedral,rod-shaped,comma-shaped or lollipop-shaped.

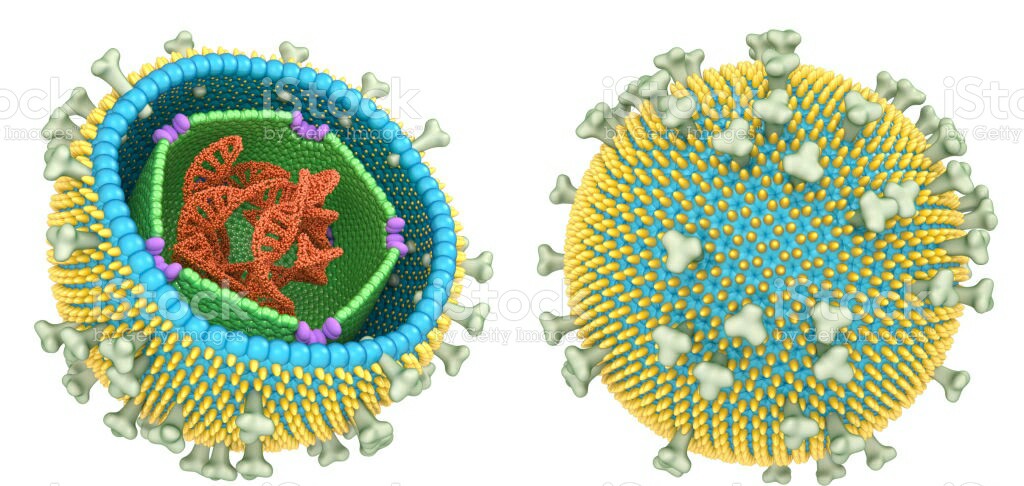
Structure- structure of all viruses is designed to meet 4 fundamental needs. A virus must be able to- a)protect its genetic material from environmental hazards when outside the host cell. b)insert its genetic material on coming in contact with a host cell. c) replicate its genome in the host cell. d)manufacture its protective structure using the limited amount of genetic information at its disposal. 1)Nucleic acid 2)capsid 3)Envelope
Host Range- The host range for a given virus may be broad or very limited. Viruses infect unicellular organisms such as mycoplasma, bacteria, and algae, and all plants and animals.
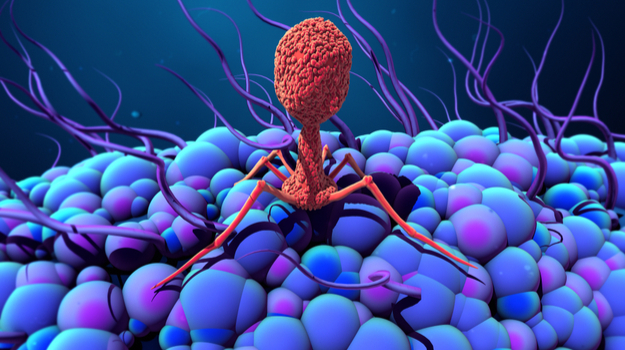
Classification based on host types. 1)Bacterial viruses. These viruses grow only within bacterial cells,which swell up and die. They are called Bacteriophages or simple phages. They were discovered in 1917 by the French scientists d’ Herelle. They are the most complex viruses. They may contain RNA or DNA in linear or circular form. The bacteriophages occur in nature wherever bacteria are found, and are specially abundant in the intestines of human and other animals.
2)plant viruses. The viruses attack the cells, disturb their metabolism and cause severe disease. They usually have linear RNA as the genetic material. The tobacco mosaic virus(TMV) is a common plant virus. Other example are southern beet mosaic virus(SBMV) ,turnip yellow virus(TYV)
3)Animal viruses. These viruses attack animal cells, and may cause fatal disease. They have DNA or RNA molecule of linear or circular form. Some animal viruses e.g., influenza and herpes viruses
Pathogenicity All living organisms(bacteria, fungi, plants and animals) are liable to infection of virus particles. Viruses act as highly pathogenic agents when in host cells. They cause diseases in humans,domestic animals as well as plants.
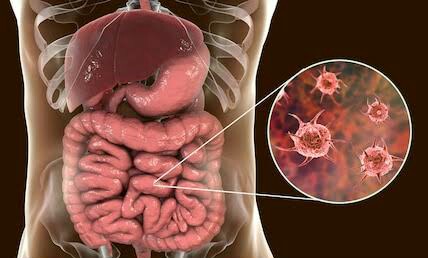
Host immune response Both cellular and humoral immune system of the host play a role in the control of viral infection. Macrophages ana lymphocytes from the major cellular response to inflammation caused by viral lesions.